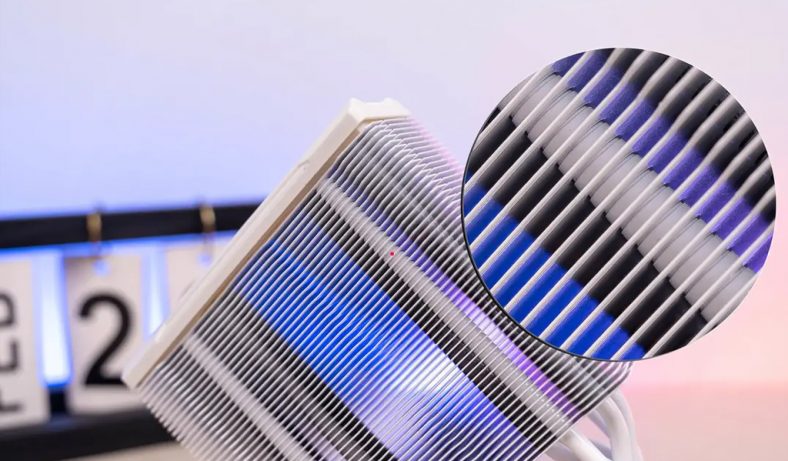
Define Of Computer Heatsink – What Is Computer Heatsink
Integrated circuits are used extensively in computer components. As we all know, high temperature is the enemy of integrated circuits. High temperature will not only cause the system to run erratically, shorten the service life, and may even cause some components to burn out. The heat that causes the high temperature does not come from outside the computer, but from inside the computer, or inside the integrated circuit.
The function of the heat sink is to absorb the heat, and then dissipate it to the inside or outside of the case to ensure that the temperature of the computer components is normal. Most heatsink absorb heat by contacting the surface of the heat-generating components, and then transfer the heat to a distance through various methods, such as the air in the chassis, and then the chassis transmits the hot air to the outside of the chassis to complete the cooling of the computer.
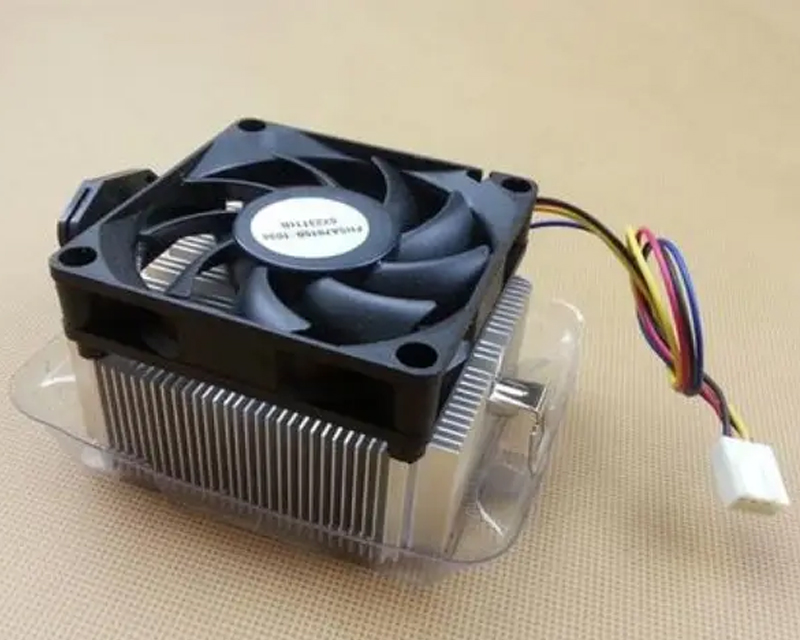

There are many types of heatsink. CPUs, graphics cards, motherboard chipsets, hard drives, chassis, power supplies, and even optical drives and memory all require heatsink. These different heatsink cannot be mixed, and the most commonly used one is the CPU heat sink.
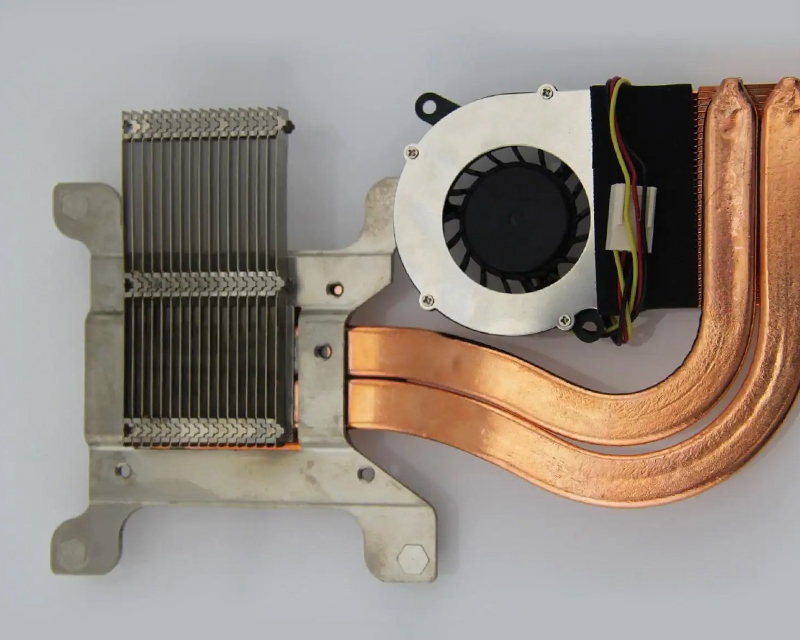
Heat sink material refers to the specific material used for the heat sink. The thermal conductivity of each material is different, arranged from high to low thermal conductivity, respectively, silver, copper, aluminum, steel.
However, if silver is used as the heat sink, it will be too expensive, so the best solution is to use copper. Although aluminum is much cheaper, it is obviously not as thermally conductive as copper (roughly just over fifty percent of copper).
Commonly used heat sink materials are copper and aluminum alloys, each of which has its own advantages and disadvantages. Copper has good thermal conductivity, but it is expensive, difficult to process, heavy (many pure copper heat sinks exceed the weight limit of CPU), small heat capacity, and easy to oxidize. Pure aluminum is too soft to be used directly. Only aluminum alloys are used to provide sufficient hardness. The advantages of aluminum alloys are low price and light weight, but the thermal conductivity is much worse than that of copper. Some heatsink take their own advantages and embed a copper plate on the aluminum alloy heat sink base. For ordinary users, the use of aluminum heat sinks is enough to meet the heat dissipation needs.
The Cooling Method Of Computer
The heat dissipation method refers to the main way that the heat sink dissipates heat. In thermodynamics, heat dissipation is heat transfer, and there are three main ways of heat transfer: heat conduction, heat convection and heat radiation. The transfer of energy in matter itself or when matter comes into contact with matter is called heat conduction, which is the most common form of heat transfer. For example, the direct contact between the CPU heat sink base and the CPU to take away heat is thermal conduction. Thermal convection refers to the heat transfer method in which the flowing fluid (gas or liquid) takes the heat away.
In the cooling system of the computer case, the “forced thermal convection” cooling method in which the cooling fan drives the gas flow is more common. Thermal radiation refers to the transfer of heat by means of ray radiation, the most common of which is solar radiation in daily life.
These three heat dissipation methods are not isolated. In daily heat transfer, these three heat dissipation methods all occur at the same time and work together.
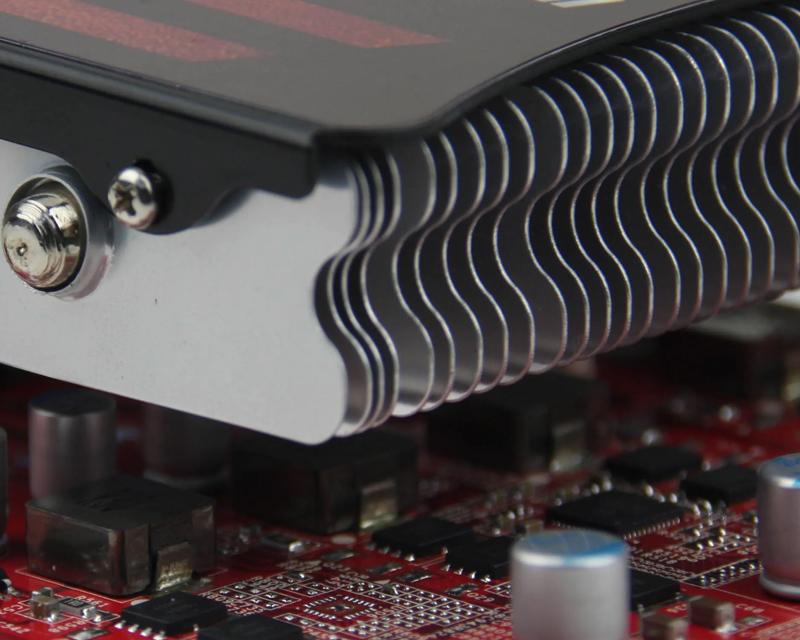
In fact, any type of heat sink will basically use the above three heat transfer methods at the same time, but the emphasis is different. For example, in an ordinary CPU air-cooled heatsink, the CPU heat sink is in direct contact with the CPU surface, and the heat on the CPU surface is transferred to the CPU heat sink through thermal conduction; the cooling fan generates airflow to take away the heat on the surface of the CPU heat sink through thermal convection;

The flow of the air also takes away the heat of the air around the CPU heat sink through thermal convection until the outside of the chassis; at the same time, all parts with high temperature will radiate heat to parts with low surrounding temperature.
The heat dissipation efficiency of the heatsink is related to the thermal conductivity of the heatsink material, the heat capacity of the heatsink material and the heat dissipation medium, and the effective heat dissipation area of the heatsink.
According to the way of removing heat from the heatsink, the heatsink can be divided into active cooling and passive cooling. To further subdivide the cooling methods, it can be divided into air cooling, heat pipe, liquid cooling, semiconductor cooling, compressor cooling and so on.
Air Cooling
Air cooling is the most common, and very simple, is to use a fan to remove the heat absorbed by the heatsink. It has the advantages of relatively low price and simple installation, but it is highly dependent on the environment. For example, its heat dissipation performance will be greatly affected when the temperature rises and overclocking.
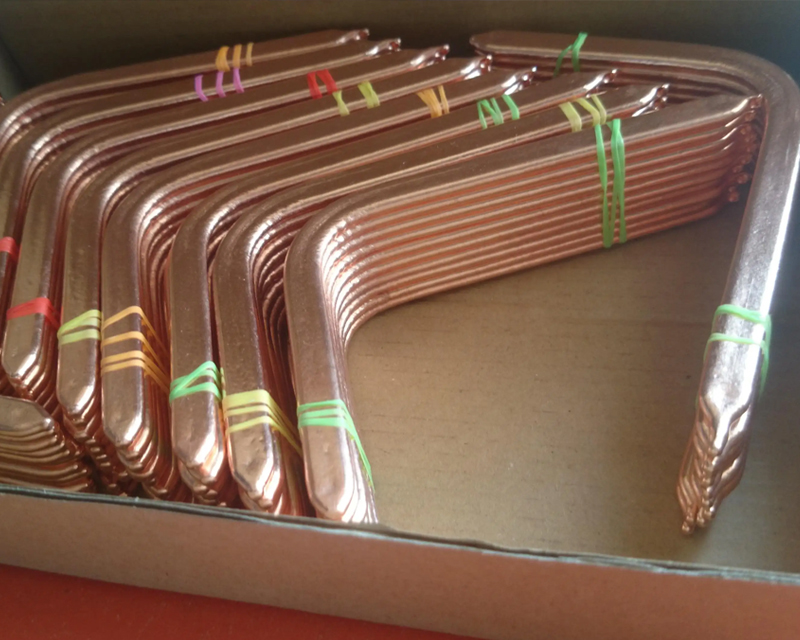


Heat Pipe
A heat pipe is a heat transfer element with extremely high thermal conductivity. It transfers heat through the evaporation and condensation of liquid in a fully enclosed vacuum tube.
It uses fluid principles such as capillary action to achieve a cooling effect similar to that of a refrigerator compressor.
It has a series of advantages such as extremely high thermal conductivity, good isothermal, heat transfer area on both sides of cold and hot can be changed arbitrarily, long-distance heat transfer, temperature control and a series of advantages, and the heat exchanger composed of heat pipes has heat transfer efficiency It has the advantages of high height, compact structure and small fluid resistance loss. Due to its special heat transfer characteristics, the tube wall temperature can be controlled to avoid dew point corrosion.
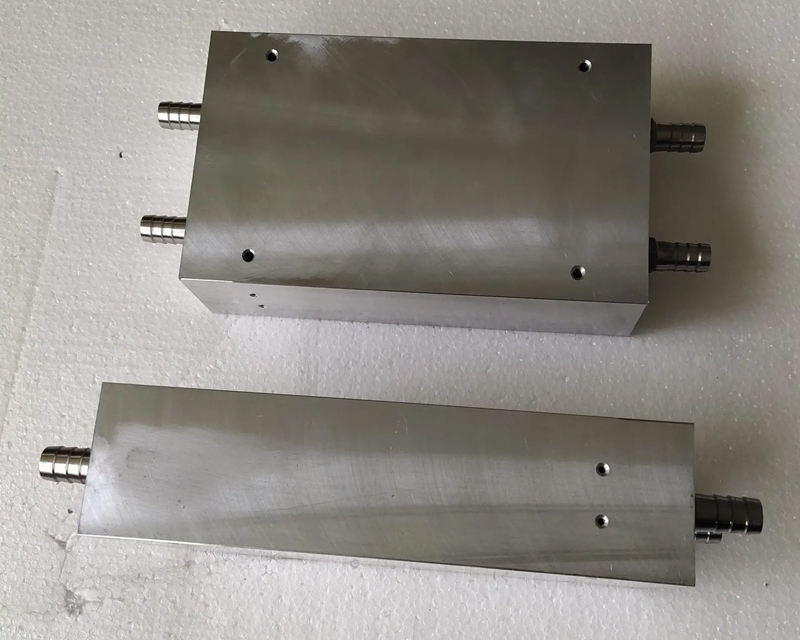
Liquid Cooling
Liquid cooling is the use of liquid to force the circulation of the heatsink to take away the heat of the heatsink driven by the pump. Compared with air cooling, it has the advantages of quietness, stable cooling, and less dependence on the environment. However, the price of heat pipes and liquid cooling is relatively high, and the installation is relatively troublesome.

The Principle Of Computer Heat Dissipation
After the heat is transferred to the top of the heat sink, it is necessary to dissipate the transmitted heat to the surrounding environment as soon as possible. For the air-cooled heat sink, it is to exchange heat with the surrounding air.

At this time, heat is transferred between two different media, and the formula followed is Q=α X A X ΔT, where ΔT is the temperature difference between the two media, that is, the temperature difference between the heat sink and the surrounding air; and α is the temperature difference of the fluid. Thermal conductivity, after the heat sink material and air composition are determined, it is a fixed value; the most important A is the contact area between the heat sink and the air.
Under the premise that other conditions remain unchanged, such as the volume of the heat sink, there will generally be However, by changing the shape of the heat sink, increasing the contact area with the air and increasing the heat exchange area, it is an effective means to improve the heat dissipation efficiency. To achieve this, the surface area is generally increased by means of a finned design supplemented by surface roughening or threads.
After the heat is transferred to the air, the temperature of the air in contact with the heat sink will rise rapidly. At this time, the hot air should take away the heat as much as possible with the surrounding cold air through heat exchange such as convection.For air-cooled heat sinks , the most important means is to increase the speed of air flow and use a fan to achieve forced convection. This is mainly related to the design of the fan and the wind speed.
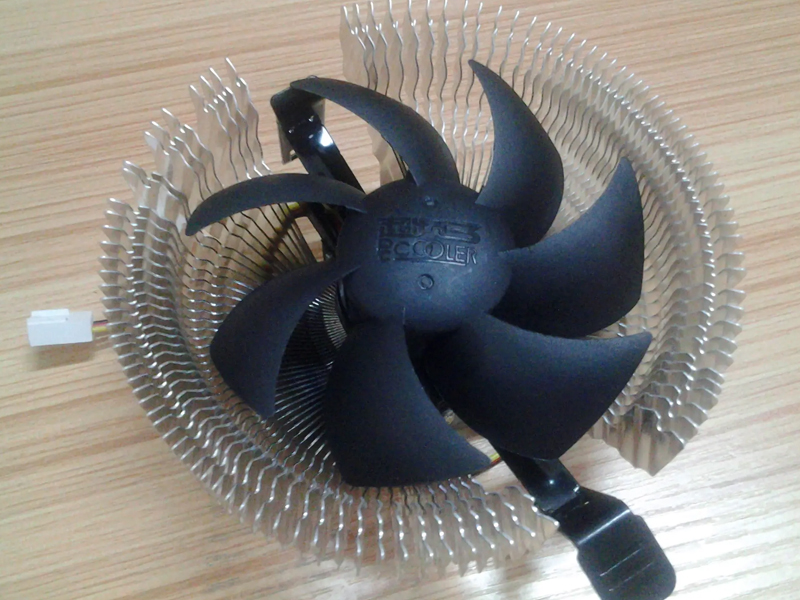

The efficiency of the heat sink fan (such as flow, wind pressure) mainly depends on the diameter of the fan blade, the axial length, the speed of the fan and the shape of the fan blade. The flow rate of the fan is mostly in CFM (Imperial system, cubic feet/minute), and a CFM is about 0.028mm3/minute flow.




